MOKE (Magneto-optical Kerr effect) magnetometry measures the polarization rotation of a polarized laser light after it has been reflected from a reflective magnetic sample; this Kerr rotation is due to magneto-optical interaction. Two different geometries are possible; polar (moment component perpendicular to the sample surface) and longitudinal (moment component parallel to the sample surface and the plane of incidence). Temperature and field control depends on the apparatus. Due to this being an optical method, MOKE magnetometry has surface sensitivity.

MOKE magnetometer at the Université Grenoble Alpes.
Example of scientific results:
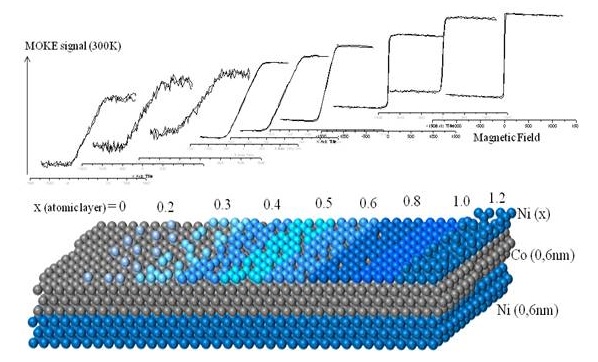
Magnetic anisotropy measurement of Ni/Co/Ni multilayer film as function of the growth of the top Ni layer. The change of the shape of the MOKE hysteresis loop shows the magnetic moment increasingly attain in-plane direction as the layer grows. (Université de Lorraine)
